
Line NOVA O-PAS - Technology

Technologies already defined as O-PAS standards

Redfish
A system comprised of O-PAS compliant components may contain thousands of components from multiple vendors. Managing platform configurations and providing platform maintenance support in this highly distributed environment requires specifying common system management functionality.
To meet the requirement of managing a multi-vendor component system, the System Management Interface is defined in O PAS Part 5. RedFish is the chosen standard to provide simple and secure management for DCNs , which enables orchestration tools detect and repair possible problems.

FDI - Field Device Integration
FDI (Field Device Integration) technology allows access to PA-DIM (Process Automation Device Information Model) for the installed base. To manage equipment, the systems use FDI, based on the OPC-UA information model and the client/server model. In this way, FDI allows for a standardized approach to device integration.

OPC-UA
The O-PAS Connectivity Framework (OCF) is a secure and interoperable communication framework. Although OCF is shown as a single network in the O-PAS architecture, actual implementations may consist of segmented networks, VLANs , firewalls, and other mechanisms to ensure security, performance, and quality of service.
O-PAS Connectivity Framework (OCF) allows interoperability between DCNs (Distributed Control Nodes). The OPC-UA standard defines the mechanisms for obtaining the information flow from DCNs . O-PAS information models are based on OPC-UA definitions. An O-PAS system must have at least one Global Discovery Server (GDS), which provides services to locate the system's TAGs.

O-PAS Signal
O-PAS Signal was based on the information model defined by FDI for process automation signals (PA DIM). We can map all the data from the information model of the two technologies.
O-PAS Signal is the main element of interoperability between distributed applications and I/O DCNs. The O-PAS Signal Alias Tag is registered in the GDS (Global Discovery Server) allowing management of the OCF network.
Access is through the Alias Tag providing the exchange of:
-
Values;
-
Timestamp;
-
Status;
-
Engineering Unit;
-
Range.

Ethernet-APL
The Ethernet APL (Advanced Physics Layer) is a network communications standard designed for industrial and automation environments. It provides a reliable and robust connectivity solution for devices and systems used in factories, industrial plants and other critical applications. With the characteristics:
-
Allows continued use of existing Twisted Pair type cables;
-
Devices powered by communication cables;
-
Long distances;
-
High speed of communication;
-
Suitable for hazardous areas;
-
Availability of connectors and other infrastructure for adverse environmental conditions;
-
Devices with high computational capacity.
The OPC Foundation has been working on developing the OPC-UA FX (Field eXchange ) protocol field devices and the OPAF is cooperating with OPC-UA FX to harmonize the two standards.

AutomationML
AutomationML is a technology for exchanging information between tools from different manufacturers in heterogeneous systems . In this way, it allows the portability of control system configurations, that is, end users can move their process control applications between tools from different suppliers
The information is exported by manufacturer A's tool, transferred and imported by manufacturer B's tool through a document with the extension “.aml ”. Manufacturer B's tool can navigate and use complex engineering information since the format is standardized.
-
Automation Markup Language, AML;
-
Open standard based on the XML standard;
-
Supports data exchange in a heterogeneous environment of engineering tools;
-
Stores engineering information;
-
It follows the object-oriented paradigm;
-
Allows you to represent plant components, both logical and physical;
-
Distributed document architecture;
-
Combines existing industrial data formats.
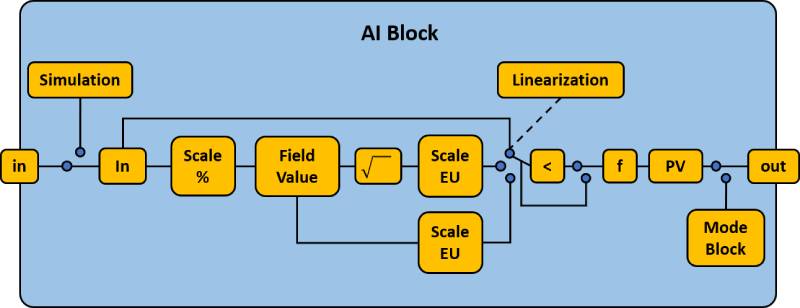
Functional Blocks
Function Blocks are software modules that consist of an information model (parameters and their data types) and calculation methods (algorithm) that are executed in O-PAS DCNs.
Function blocks are available in two profiles: IEC-61131 for periodic execution and IEC 61499 for event-based execution.
The development of the IEC-61131 O-PAS function blocks is based on the FOUNDATION Fieldbus technology function blocks. This decision is due to more than 20 years of use in the field.

Docker
Containers are a virtualization method at an operating system level that allows you to run an application and its dependencies in processes with isolated resources. Containers allow you to easily package an application's code, configurations, and dependencies into building blocks that provide environmental consistency, operational efficiency, developer productivity, and version control.
Docker is an open-source technology that allows you to create, run, test and deploy distributed applications within software containers.
Cyber Security - IEC 62443
Although there are several cybersecurity standards, they are positioned differently in relation to considerations about the role of the operator and supplier and the technical or managerial aspects of security.
IEC 62443 is the most complete, covering most industrial cybersecurity challenges, therefore is the option adopted by the O-PAS standard, being the set of standards that aim to guide industrial control and automation systems (IACS) for safe operation, providing guidelines that include:
-
Define common terms, concepts and models that can be used by all interested parties;
-
Help asset owners determine the level of security needed;
-
Establish a common set of requirements and a cybersecurity lifecycle methodology for product developers;
-
Define the risk assessment processes that are critical to protecting control systems.
"We use essential cookies and similar technologies in accordance with our Privacy Policy and by continuing to browse, you agree to these conditions." Read more







